GST
-Mrs. Nishanthi.S
Assistant Professor

GST is a transformational tax reform in our country since independence. It is an indirect tax that is imposed on goods as well as services. GST is particularly designed to replace the indirect taxes levied on goods and services by the Centre and States. GST can be termed as “One Tax, One Nation and One Market”. GST is a highly compliance driven law.GST is one indirect tax for the whole nation, which willmake India one unified common market.GST is a single tax on the supply of goods and services, right from the manufacturer to the consumer. Under this system, a single product will be taxed at the same rate in every corner of the country and so honorable Prime MinisterNarendra Modi hailed it as a “GREAT STEP BY TEAM INDIA” that will help transform the economy, bring in TRANSPARENCY and bring in the system of “ONE COUNTRY ONE TAX”.But still it does not mean that every item will be charged at the same price. Evidentlythe daily essentialwill be charged at a lower rate than the luxuries, but a single luxury product or an individual necessity good will be charged the same rate throughout the country.More than 160 countries have already introduced GST/ National Level VAT.Canada and Brazil only have dual GST.
CURRENT TAX SYSTEM AND PROPOSED TAX SYSTEM:
CURRENT INDIRECT TAX STRUCTUREPROPOSED DUAL GST MODEL
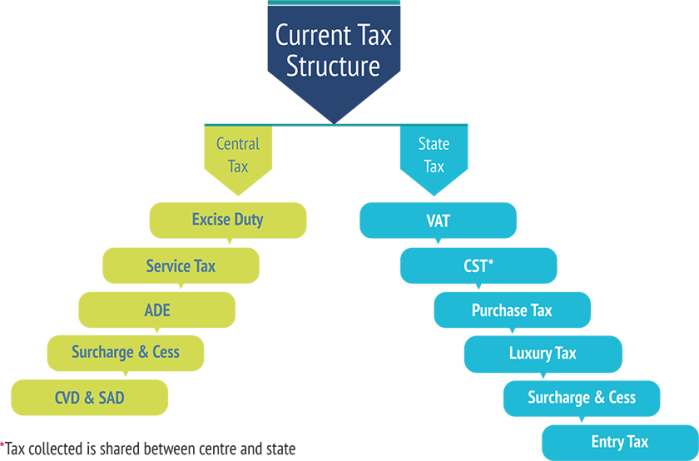
The following items will be replaced by GST which is currently imposed by Centre:-
- Central Excise duty
- Duties of Excise (Medicinal and Toilet Preparations)
- Additional Duties of Excise (Goods of Special Importance)
- Additional Duties of Excise (Textiles and Textile Products)
- Additional Duties of Customs (commonly known as CAD)
- Special Additional Duty of Customs (SAD)
- Service Tax, Central cess and surcharge
The following items will be replaced by GST which is currently imposed by State:-
- State VAT
- Central Sales Tax
- Luxury Tax
- Entry Tax (other than those in lieu of Octroi)
- Entertainment Tax (not levied by the local bodies)
- Taxes on advertisements
- Taxes on lotteries, betting and gambling
- State cess and surcharges, as they relate to supply of goods or services
- Stamp Duty & Registration Fees
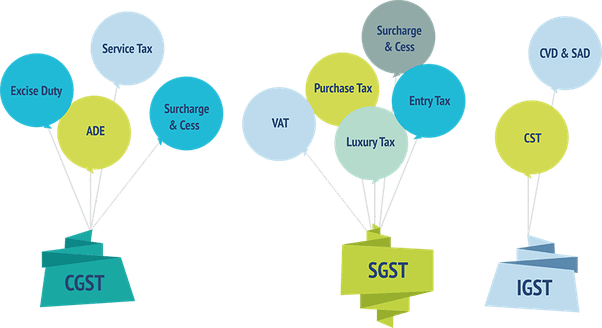
The proposed tax system will take the form of “dual GST” which is concurrently levied by central and state government. This will comprise of:
- Central GST (CGST) which will be levied by Centre
- State GST (SGST) Which will be levied by State
- Integrated GST (IGST) – which will be levied by Central Government on inter-State supply of goods and services.
GST IMPLICATIONS
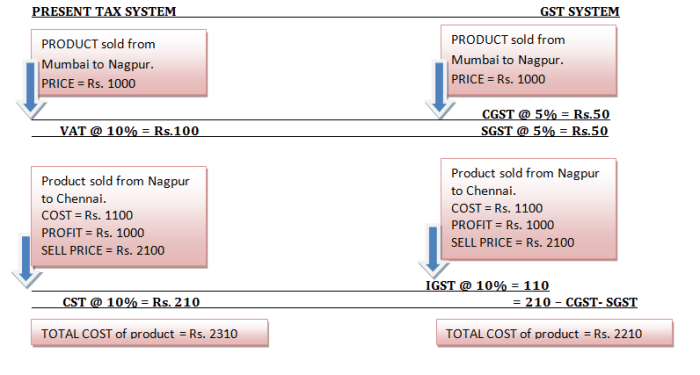
Under the current, non GST regime the indirect tax rate on goods is 27%-32% and on services its 15%. Under the proposed GST regime the expected GST rate would be 18%-22% where the cost of goods will go down and the cost of services will rise. The products like Groceries, Two-Wheelers, Small Cars, SUV, Consumer Electronics, Movie Tickets etc., will get cheaper and products like Air-Ticket, Mobile Phone, Insurance Premium, Eating-Out etc., will get costlier.Among all Petroleum products, Entertainment and amusement tax levied and collected by panchayat /municipality/district council, Tax on alcohol/liquor consumption, Stamp duty, customs duty,Tax on consumption and sale of electricity are exempted.
CONCLUSION
To conclude it is very encouraging that the GST bills are finally passed and on its way to become to make a nation proud. Therudimentary planning behind introducing GST is to convert India into a single market. This might have a positive impact on GDP of India and help to boost the Indian economy. One of the biggest taxation reforms in India – the Goods and Service Tax (GST) — is all set to integrate State economies and boost overall growth through a lower tax rate by increasing the tax.
