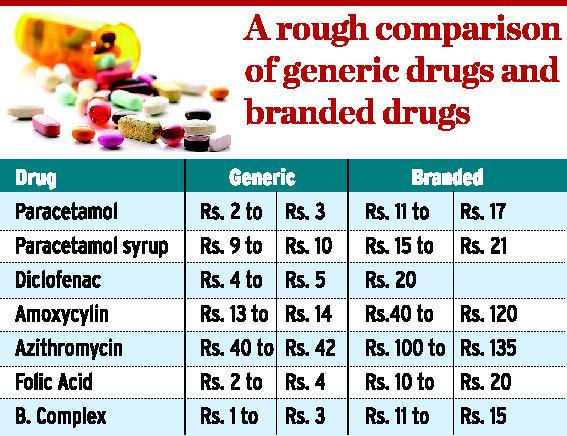
How to profit from Mutual Funds
– S.SARAVANAN, Assistant Professor, SIMS
If you want to go to Goa from Mumbai, there are several vehicular options. You can travel by airplane, drive in car, take a train or a bus, or sail in a ship. Similarly when we want to make any kind of investment, there are different investment vehicles, e.g. mutual fund, portfolio management services, “direct” (investing on your own), insurance, etc.
Goa is the destination and airplane, car, bus, train, ship, etc are vehicles. Similarly, debt, equity and property are asset classes, and mutual funds, PMS and insurance are investment vehicles.
It is important to clarify here that property includes real estate, bullion, collectibles, art, etc. To invest in debt, equity and property we have to choose investment vehicles, which suit our requirement.
In earlier times, “direct” was the only investment vehicle available. If we wanted to buy fixed deposit/bond we had to apply on our own. Similarly, when we wanted to buy shares, we had to call up stock brokers, who would procure shares on our behalf and same was the case with property.
The cost involved in “direct” buying is least amongst all investment vehicles. However, we need to have skills and time to use this form of investing. Another investment vehicle is a mutual fund. Mutual fund works on the concept of pooling in money. Assume there are 5 to 6 friends who want to invest money in a particular asset class say equity. Also assume they do not have skills and time.
However, one of them knows an expert who regularly invests in the stock markets. All these friends go to an expert and give him their investment amount. The expert invests on their behalf. If there is profit in investment, they all benefit and if there is any loss, they suffer.
Experts get certain fee for investing on their behalf. This is the concept of a mutual fund. Investing in a mutual fund is slightly expensive than “direct” form of investing. However, the decision-making and procedure of investing is transferred to the mutual fund company.
Insurance, as an investment vehicle, works somewhat similar to mutual fund as far as ULIPs (Unit-Linked Insurance Policies) are concerned. While traditional insurance plans invest only in debt-based products and are not market linked, ULIP invests in debt, equity as well as a combination of the two.
The only difference in the case of insurance is that expenses charged by the insurance company are much higher that most other investment vehicles.
PMS is usually tailor-made for your needs. Based on your financial goals, portfolio managers create an investment portfolio for you. For creating and maintaining your portfolio, the manager charges fees. Also if your portfolio earns profit beyond a certain amount, then the portfolio manager shares the profit. However, if there are losses then the same is charged to your account only.
While choosing any investment vehicle keep in mind your skills, time available with you to create and maintain your investments and costs involved.
If you have the skills and time available with you then “direct” form of investing is ideal as it has least of costs amongst all other vehicles.
On the other hand, insurance is the most expensive investment vehicle and hence it should be kept away from as far as possible.
PMS works better for wealthy (high net worth) individuals. Although profits have to be shared, there is also the advantage of getting tailor-made portfolio. Only catch is to ensure that portfolio created and maintained for you is tailor-made and that the PMS is not another mutual fund scheme, where all investors get the same portfolio.
For small and medium investor who does not have the skills or the time mutual funds seem the best option.
Currently, in India, we have mutual funds which invest in two asset classes, debt and equity. However, in the very near future there is a likelihood of having mutual funds, which will invest in gold as well as real estate.